WordPress User Roles and Permissions: Navigating the Web of Access Control

WordPress User Roles and Permissions with its user-friendly interface and robust features, powers millions of websites worldwide. One integral aspect of managing a WordPress site effectively is understanding and utilizing WordPress user roles and permissions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of WordPress user roles from the default roles provided by WordPress to customizing roles for specific needs.
Introduction WordPress User Roles and Permissions
Simple and flexible, WordPress is one of the most popular content management systems (CMS). WordPress User roles and permissions determine the actions that users can perform on a website. which are central to its functionality. Maintaining a secure and efficient WordPress site requires understanding the nuances of WordPress user roles whether you are the site owner, administrator or contributor.
Understanding WordPress User Roles and Permissions
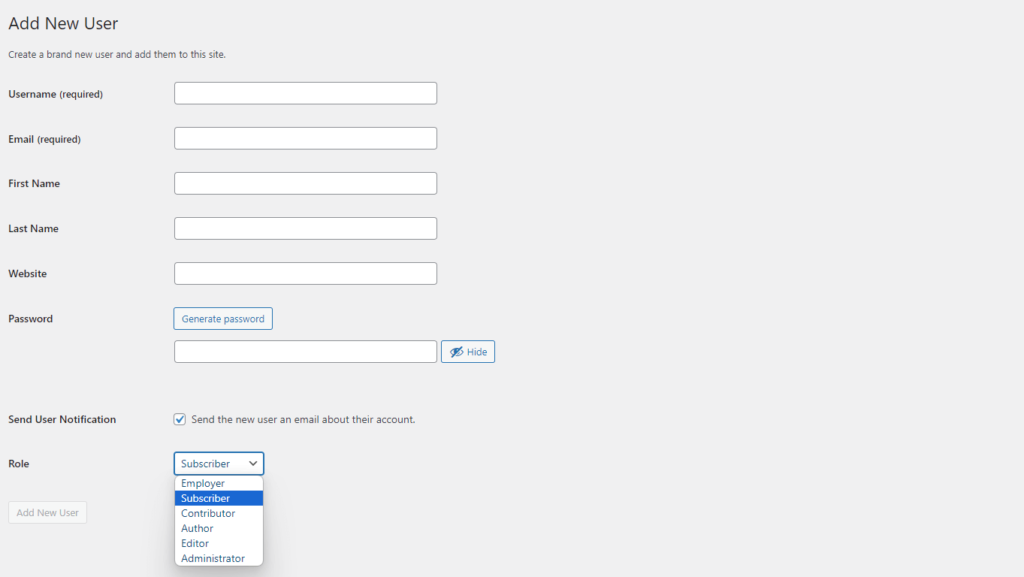
how to add a new user role in wordpress
WordPress comes with five default user roles, each serving a unique purpose.
- Login Your admin panel -> Users – > Add New User
| 1 | Administrator | The omnipotent role with full control over the site. |
| 2 | Editor | Manages and publishes content, but can’t alter site settings. |
| 3 | Author | Creates and publishes their content, restricted from site settings. |
| 4 | Contributor | Writes content but needs approval for publication. |
| 5 | Subscriber | Can only manage their profile and comment on posts. |
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each role sets the foundation for effective user management.
Customizing WordPress User Roles
Tailoring user roles to fit specific needs is a powerful feature in WordPress.
- To create a custom role, navigate to the functions.php file and define capabilities.
- Assign capabilities based on desired access levels and responsibilities.
Managing User Permissions
Decoding Permissions in WordPress
Permissions determine what users can and cannot do on a WordPress site.
- Illustrating how permissions relate to user roles.
- Highlighting the significance of a well-defined permission structure.
Importance of WordPress User Roles in Website Security
User roles play a crucial role in fortifying your WordPress website security.
- Restricting access to sensitive areas prevents unauthorized modifications.
- Tips on leveraging user roles to enhance overall site security.
WordPress User Role Best Practices
Adhering to best practices ensures a smooth user role management experience.
- Assigning roles based on responsibilities, not just hierarchy.
- Steering clear of over-permissioned roles to mitigate security risks.
Plugins for Advanced WordPress User Role Management
Elevating User Role Functionality with Plugins
Discover plugins that enhance WordPress user role management capabilities.
- Role Editor, Members, and User Role Editor: features and benefits.
- Selecting the right plugin based on site requirements.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Addressing User Role Management Challenges
Identifying common challenges and offering practical solutions.
- From role conflicts to permission discrepancies, troubleshoot effectively.
- Ensuring a seamless user role management experience.
User Education on WordPress Roles
Promoting Responsible Use
Highlighting the importance of educating users on their assigned roles.
- Preventing unintentional actions that may affect site functionality.
- Encouraging responsibility and adherence to role-specific guidelines.
Capability vs. Role Table
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| create_sites | Y | |||||
| delete_sites | Y | |||||
| manage_network | Y | |||||
| manage_sites | Y | |||||
| manage_network_users | Y | |||||
| manage_network_plugins | Y | |||||
| manage_network_themes | Y | |||||
| manage_network_options | Y | |||||
| upload_plugins | Y | |||||
| upload_themes | Y | |||||
| upgrade_network | Y | |||||
| setup_network | Y | |||||
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
| activate_plugins | Y | Y (single site or enabled by network setting) | ||||
| create_users | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| delete_plugins | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| delete_themes | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| delete_users | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| edit_files | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| edit_plugins | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| edit_theme_options | Y | Y | ||||
| edit_themes | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| edit_users | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| export | Y | Y | ||||
| import | Y | Y | ||||
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
| install_plugins | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| install_themes | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| list_users | Y | Y | ||||
| manage_options | Y | Y | ||||
| promote_users | Y | Y | ||||
| remove_users | Y | Y | ||||
| switch_themes | Y | Y | ||||
| update_core | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| update_plugins | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| update_themes | Y | Y (single site) | ||||
| edit_dashboard | Y | Y | ||||
| customize | Y | Y | ||||
| delete_site | Y | Y | ||||
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
| moderate_comments | Y | Y | Y | |||
| manage_categories | Y | Y | Y | |||
| manage_links | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_others_posts | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_others_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_published_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| publish_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_others_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_published_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_others_posts | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_private_posts | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_private_posts | Y | Y | Y | |||
| read_private_posts | Y | Y | Y | |||
| delete_private_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| edit_private_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| read_private_pages | Y | Y | Y | |||
| unfiltered_html | Y | Y (single site) | Y (single site) | |||
| unfiltered_html | Y | Y | Y | |||
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
| edit_published_posts | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| upload_files | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| publish_posts | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| delete_published_posts | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| edit_posts | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| delete_posts | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Capability | Super Admin | Administrator | Editor | Author | Contributor | Subscriber |
| read | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
Conclusion
Summarizing the key takeaways from our exploration of WordPress user roles and permissions.
- Emphasizing the role of user roles in site security, collaboration, and efficiency.
- Empowering site administrators to make informed decisions in user role management.
FAQ
Can I create a custom user role for a specific task on my WordPress site?
Yes, WordPress allows you to create custom user roles tailored to your specific needs. This provides flexibility in managing various tasks efficiently.
How often should I audit user role changes on my site?
Regular audits are recommended, especially after major updates or changes. This ensures accountability and helps identify and rectify any discrepancies promptly.
What’s the difference between an Editor and an Author in WordPress?
While both can create and manage content, an Editor has broader permissions, including the ability to edit and publish others’ content. Authors can only manage their own content.
Can I revert a user role change if a mistake occurs?
Yes, you can revert a user role change. Plugins and manual methods, like database adjustments, allow you to undo role modifications and maintain site integrity.