Deep Dive into Full text Search Implementation in Node js with Elasticsearch
In today’s data-driven world, efficient search functionalities are pivotal for applications dealing with large volumes of unstructured data. Full-text search engines like Elasticsearch have become integral in enabling developers to implement robust search capabilities efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the implementation of full-text search using Elasticsearch in Node.js
Introduction to Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a powerful, distributed search and analytics engine built on top of Apache Lucene. Its versatility lies in its ability to handle a variety of data types, scalability, and high-speed search capabilities. Elasticsearch’s RESTful API and JSON-based query DSL make it easily accessible and flexible for developers.
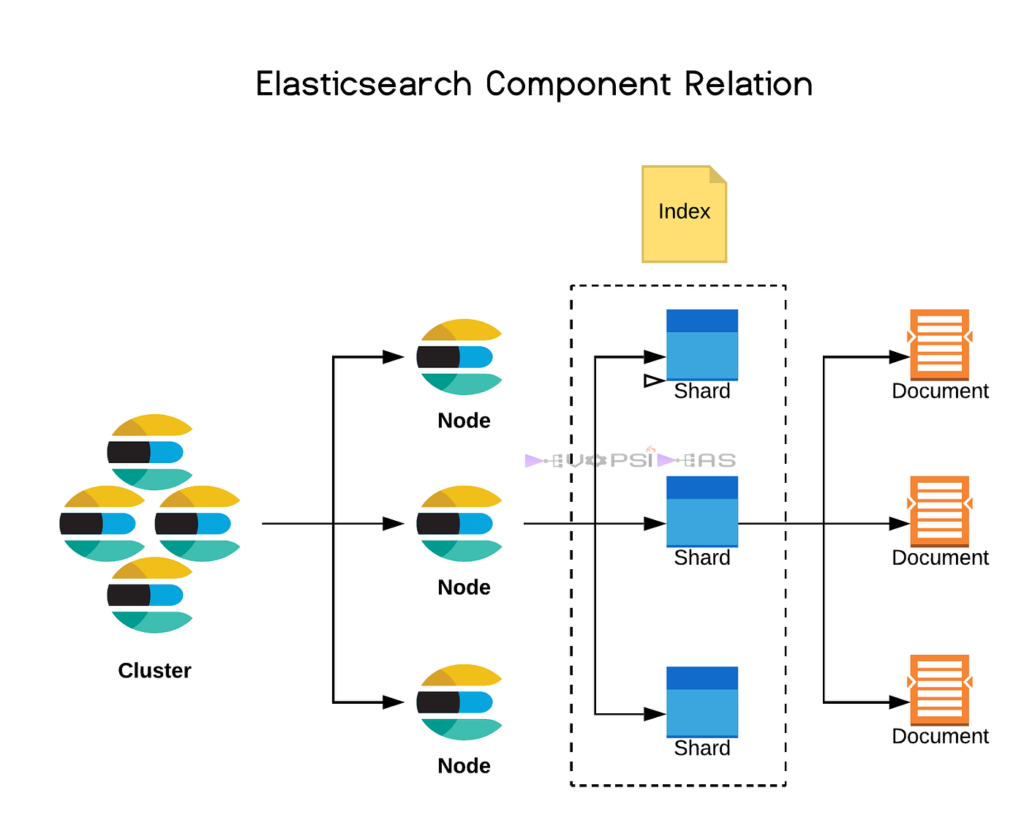
Key Components of Elasticsearch:
Use Cases and Applications:
Importance and Popularity:
Importance in Modern Applications
Efficient search functionality has become a cornerstone of modern applications. Users expect intuitive, lightning-fast search experiences, making Elasticsearch’s capabilities crucial for providing such experiences.
Adaptability and Versatility
Elasticsearch’s adaptability to various use cases ranging from e-commerce search, log analysis to enterprise-level applications has contributed to its popularity. Its versatility in handling structured and unstructured data makes it a go-to choice for developers.
Open Source and Community Support
Being open source has fostered a vibrant community around Elasticsearch. This community support, combined with frequent updates and improvements has contributed significantly to its widespread adoption.
Big Data and Analytics
The explosion of big data and the need for real-time analytics have propelled the popularity of Elasticsearch. Its ability to handle large volumes of data efficiently and perform quick, sophisticated queries aligns perfectly with these demands.
Setting Up Elasticsearch
Node js and Elasticsearch Integration
Installing Elasticsearch Client for Node js.
To interact with Elasticsearch from a Node Js application, utilize the official Elasticsearch client for Node.js, known as elasticsearch.js. Install it via npm:
npm install @elastic/elasticsearchConnecting to Elasticsearch
Create a connection to Elasticsearch within your Node.js application:
const { Client } = require('@elastic/elasticsearch');
const client = new Client({ node: 'http://localhost:9200' });Replace ‘http://localhost:9200‘ with your Elasticsearch instance’s URL.
Indexing Data
Elasticsearch organizes data into indices, somewhat analogous to databases in relational databases. To begin indexing data:
creating An Index
async function createIndex() {
await client.indices.create({
index: 'your_index_name'
});
}Adding Documents
async function addDocument() {
await client.index({
index: 'your_index_name',
body: {
title: 'Sample Title',
content: 'This is a sample document content'
}
});
}Searching Data
Elasticsearch’s powerful querying capabilities allow for complex searches on indexed data.
Simple Text Search
async function simpleSearch() {
const { body } = await client.search({
index: 'your_index_name',
body: {
query: {
match: { content: 'sample search query' }
}
}
});
console.log(body.hits.hits);
}Full-text Search with Query String Query
async function fullTextSearch() {
const { body } = await client.search({
index: 'your_index_name',
body: {
query: {
query_string: {
query: 'full-text search query'
}
}
}
});
console.log(body.hits.hits);
}Advance Feature
Aggregations
Elasticsearch allows aggregations to summarize and analyze data.
async function performAggregation() {
const { body } = await client.search({
index: 'your_index_name',
body: {
aggs: {
avg_content_length: {
avg: { field: 'content.length' }
}
}
}
});
console.log(body.aggregations);
}Pagination and Sorting
Implement pagination and sorting for search results.
Analyzers and Tokenizers
Customize text analysis using analyzers and tokenizers to handle various languages and special cases.
Advantages of Elasticsearch:
Scalability and Performance
Elasticsearch’s distributed nature allows it to scale horizontally, handling large amounts of data across multiple nodes. Its inverted index structure enables lightning-fast search queries, making it ideal for real-time applications.
Full-text Search Capabilities
The ability to perform complex full-text searches across a wide range of data types, including structured and unstructured data, sets Elasticsearch apart. It supports fuzzy searches, partial matching and relevance-based scoring.
Real-time Data Analysis
Elasticsearch’s near real-time capabilities allow for instant indexing and search, making it suitable for applications that require quick data retrieval and analysis.
Rich Querying Functionality
It’s query DSL provides a versatile toolkit for crafting various queries, including aggregations, filters, geospatial queries and more, facilitating precise data retrieval.
Ecosystem and Integration
The Elasticsearch ecosystem includes various plugins, libraries and integrations with tools like Logstash and Kibana, forming the ELK stack. Additionally, its RESTful API enables easy integration with different programming languages and frameworks.
Disadvantages of Elasticsearch:
Complexity in Configuration
Setting up and configuring Elasticsearch for optimal performance in larger-scale deployments can be complex. Managing indexing strategies, shard allocation and cluster health might require expertise.
Resource Intensive
Elasticsearch can be resource-intensive, particularly when dealing with larger datasets or complex queries. It might demand significant memory, storage and processing power.
Data Security
Securing data in Elasticsearch requires attention to security best practices. Without proper configurations, data might be vulnerable to unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Implementing full-text search with Elasticsearch in Node js opens doors to powerful search functionalities. Its rich querying capabilities, scalability and speed make it a preferred choice for diverse applications. By leveraging Elasticsearch’s features effectively, developers can enhance search experiences and handle vast amounts of data seamlessly.
Implementing a full-text search using Elasticsearch in Node.js requires understanding indexing, querying and utilizing advanced features. With Elasticsearch’s flexibility and Node.js integration, developers can build sophisticated search functionalities for their applications, empowering users to find information efficiently.
FAQ
Is Elasticsearch suitable for small scale applications?
Yes, Elasticsearch is scalable and can be used in small-scale applications too. Its flexibility allows it to scale as the application grows.
How does Elasticsearch handle data redundancy?
Elasticsearch uses sharding and replication to handle data redundancy, ensuring fault tolerance and high availability.
Can Elasticsearch be used for real time data?
Yes, Elasticsearch excels in real-time data analysis and retrieval due to its distributed nature and speed.





